Elastomer vs. Silicone: A Comprehensive Comparison: Uncovering the Key Truths of Material Selection
In modern manufacturing, material selection determines a product’s lifespan and market competitiveness. Many people often confuse “elastomer” and “silicone,” even considering them synonymous. While silicone is a type of elastomer, it differs fundamentally from traditional thermoplastic elastomers (TPE, TPR, TPU, etc.). This article delves into the essential differences, advantages and disadvantages, applicable scenarios, and purchasing recommendations between the two. It aims to help product designers, purchasing managers, and entrepreneurs better understand the differences between elastomers and silicones, enabling them to make optimal decisions in new product development and material selection.
What is an elastomer?
Elastomers generally refer to materials that return to their original shape after the removal of an external force. However, materials exhibiting elasticity are not necessarily elastomers. Elastomers are polymer materials that deform significantly under weak stress and then quickly return to a near-original state and size after stress relaxation.


Elastomers are a general term for a class of polymer materials with high elasticity. Their core characteristics are:
Scientific classification of elastomers
Based on their material properties, elastomers can be classified as follows:
What is silicone gel/silicone rubber?
Silicone is a special synthetic polymer elastomer whose backbone consists of alternating Si-O-Si bonds. Silicone atoms are typically attached to two organic groups.
Ordinary silicone rubber is primarily composed of siloxane chains containing methyl groups and a small amount of vinyl groups. The introduction of phenyl groups can improve silicone rubber’s high and low temperature resistance, while the introduction of trifluoropropyl and cyano groups can enhance its heat and oil resistance.

Silicone rubber exhibits excellent low-temperature resistance and can generally operate at temperatures as low as -60°C. The introduction of phenyl groups increases its low-temperature resistance to -73°C. Silicone rubber also boasts outstanding heat resistance, capable of long-term operation at 180°C and maintaining elasticity for weeks or longer at temperatures slightly above 200°C. It can also withstand transient temperatures exceeding 300°C. Silicone rubber also offers excellent breathability, with the highest oxygen transmission rate among synthetic polymers. Furthermore, silicone rubber is physiologically inert and non-clotting, making it widely used in the medical field.
Silicone rubber is generally classified by its pre-cured form into solid silicone rubber and liquid silicone rubber; by its vulcanization temperature into room temperature vulcanized silicone rubber and high temperature vulcanized silicone rubber.


Based on the monomers used, it can be categorized into methyl vinyl silicone rubber, methylphenyl vinyl silicone rubber, fluorosilicone, and nitrile silicone rubber.
Based on performance and application, it can be further divided into general-purpose, ultra-low-temperature-resistant, ultra-high-temperature-resistant, high-strength, oil-resistant, and medical types. Silicone rubber is categorized into heat-vulcanized (high-temperature vulcanized silicone HTV) and room temperature vulcanized (RTV). RTV silicone rubber is further divided into polycondensation-reaction-based and addition-reaction-based types. High-temperature silicone rubber is primarily used in the manufacture of various silicone rubber products, while room-temperature silicone rubber is primarily used as adhesives, potting materials, or molds.
Hot-vulcanized silicone rubber is the most widely used type, and is further divided into methyl silicone rubber (MQ), methyl vinyl silicone rubber (VMQ, which has the largest usage and product grades), and methyl vinyl phenyl silicone rubber (PVMQ) (which is resistant to low temperatures and radiation). Other types include nitrile silicone rubber and fluorosilicone rubber. These rubbers are widely used in the infant and childcare, medical, electronics, and aviation industries.
As can be seen from the above, all silicones are elastomers, but not all elastomers are silicones.
Z.S.R is a full-service custom silicone products manufacturer offering end-to-end customization, from mold development, prototyping to mass production and packaging.
Contact Z.S.R if you have any silicone products need to manufacture.
Why differentiate between elastomers and silicone?
Silicone is more suitable for food and medical-grade applications. It offers extremely high temperature resistance (-60°C to 250°C), ozone resistance, UV resistance, and is non-toxic and environmentally friendly. However, it is costly, complex to process, and has lower wear resistance than ordinary elastomers. Its mechanical strength is limited, and silicone products are generally more expensive. Silicone also has higher material and mold costs than TPE/TPR.

TPE/TPEE offer lower costs, diverse physical properties (oil resistance, wear resistance, and good elasticity), and mature processing. However, most offer low temperature resistance, are susceptible to aging, are flammable, and have limited chemical stability. They are more suitable for consumer electronic components requiring high-volume, low-cost injection molding.


Certifications and Regulations:
Medical devices and baby products often require certifications such as FDA/LFGB/ISO10993, which silicone products are more likely to meet. TPE, however, is often used for ordinary sports tracker housings and grips.
When the people should be considered Elastomer vs silicone differences?
During the new product development phase: Product designers/industrial designers/startup founders need to select the right material based on the product’s positioning, carefully considering material performance, processing technology, and applicable scenarios. For example, for baby products, medical consumables, and kitchen supplies, early material decisions are necessary to avoid mistakes, and silicone is the preferred material.
During the cost optimization phase: Purchasing managers evaluate suppliers, control costs, and ensure delivery dates, or need to balance performance and cost. When replacing silicone to reduce price, they may consider TPE.
During the functional upgrade phase: For example, silicone is superior in high-temperature and chemical-resistant environments.
End consumers and brands are increasingly concerned about “environmental protection, health, and safety.” They are placing great emphasis on product lifespan, safety, and comfort. Therefore, when selecting products, the material used must be carefully considered.
Z.S.R’s team work with the different industries brand’s Owners, products development managers, products managers, products designers together and offer them OEM ODM solution from molded silicone products design, prototyping to silicone products contract manufacturing, printing, package to ensure their silicone projects success. We have the capability for producing silicone tooling, producing HTV Silicone products, LSR molded silicone products, Molded multi-colored Silicone products.
Contact Z.S.R start Your Custom Silicone Projects.
Custom Silicone Products | OEM/ODM Service
Where are the applications of Elastomer vs silicone?
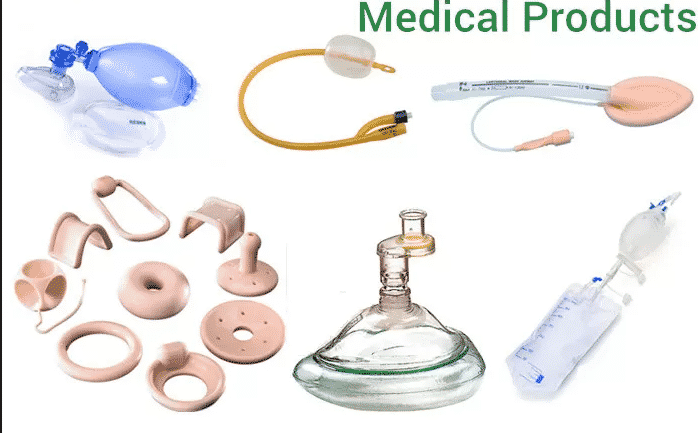
Silicone: Medical devices, maternal and child products, kitchenware, food contact materials, high-temperature seals, electronic component sealing and protection. Examples include pacifiers, kitchenware, medical catheters, sealing rings, and aviation components.
Elastomers (TPE/TPR): handle covers, mobile phone cases, toys, industrial equipment, oil and gas pipelines, sports equipment, protective gear, automotive seals, industrial conveyor belts, low-temperature rubber parts, and cost-sensitive consumer goods.
Z.S.R’s Precision Silicone mold /tooling ,Silicone Compression molding(32sets), Silicone over-molding, Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection molding: LSR molding, Liquid silicone rubber over molding, LSR Multi-Shot (LSR/Thermoplastic/Metal), silicone Dripping molding, capabilities allow us to manufacture any type silicone rubber products for your company’s needs in an infinite variety of design, function, material, structure, shape, sizes, color, logo, pattern, package, label configurations etc. Custom silicone products manufacturing for diverse needs of worldwide—from sketch to final delivery, ensuring quality silicone products for different industry application from industrial, consumer, commercial to medical.
How to produce silicone or elastomer products
Silicone:
Production methods primarily include compression molding, injection molding, and extrusion.
The process of producing silicone products involves several steps from silicone products Design Concept, Material Selection, Prototypes Development, logo Printing or Branding, Silicone Tooling and Mold, Material Mixing and Preparation, Silicone Molding and Shaping, Curing and Cooling, Demolding, Quality Control, Cleaning and Packaging to shipping for creating personalized and branded silicone molded products or other silicone products.
While the process cycle is relatively long and mold costs are high, the product’s precision and performance are stable.
Z.S.R Own 32 sets of the compression molding machine, 12 sets of liquid silicone rubber molding machine, 8 sets of co-injection silicone molding machines for producing, Ensure the stable production capacity of your products.
Elastomer (TPE/TPR/TPU):
Injection molding is often used, offering a fast process speed and allowing for secondary injection molding with hard plastics such as PP/ABS, making it suitable for large-scale production.
How to Choose Elastomer or Silicone?
- Based on Operating Temperature: If the product needs to withstand high or low temperatures, or is in contact with food or for medical applications, silicone is preferred.
- Based on Physical Performance Requirements: For wear resistance and oil resistance, choose specialized elastomers; for softness, non-toxicity, and easy cleaning, choose silicone.
- Based on production quantity: For high-volume consumer electronics, toys, or general anti-slip applications, choose TPE, TPR, or TPU.
- Based on budget: Elastomers are lower cost and economical for mass production; silicone is suitable for high-value-added products.
How much cost of silicone or elastomer products?
Silicone: Raw material price is 5-30 USD/kg (depending on grade and certification). Mold costs are high, especially for food-grade and medical-grade materials. The processing also requires stringent equipment, resulting in higher overall costs. This makes it suitable for high-value-added products.
TPE/TPR: Elastomer raw material prices are relatively low, ranging from 3-8 USD/kg. Mold and processing equipment costs are moderate, making it suitable for mass-market consumer goods.
How to control quality of silicone or elastomer products?
Silicone
Material: Control raw material quality during procurement and select certified suppliers; choose raw materials with FDA and LFGB certifications.
Strictly monitor the production process, focusing on mixing uniformity and vulcanization process control.
Finished product testing ensures that physical properties (e.g., tensile strength, tear strength, and hardness) meet standards.
Elastomers
Focus on hardness deviation, springback, and adhesion to the substrate.
How to clean silicone or elastomer products?
TPE/TPR products: Avoid high-temperature cleaning. They are easily corroded by oil and grease, so they are best cleaned with warm water and a neutral detergent. Wipe frequently with a damp cloth to avoid corrosion from organic solvents.
Silicone: Silicone has excellent chemical resistance and can be sterilized with high-temperature steam and multiple washes. It can be sterilized with boiling water or high-temperature steam. It resists aging over time and is suitable for the medical and food industries.
More FAQs
1. Which is more environmentally friendly, silicone or ordinary elastomers?
Silicone is stable and free of volatiles, making it less recyclable. However, it is non-toxic and odorless, making it more in line with sustainable development trends. Overall, its environmental performance is superior to some synthetic elastomers, but the specifics depend on the material formulation.
2. Can silicone replace all TPEs?
No. TPE remains the preferred material for high-volume, low-cost products.
3. Which is more resistant to high temperatures, elastomer or silicone?
Silicone’s high-temperature resistance far exceeds that of most elastomers, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
4. Is silicone suitable for children’s toys?
Food-grade and medical-grade silicones are highly suitable, being safe, non-toxic, and soft to the touch.
5. What can be done about elastomer products that easily deform?
Adjust the curing degree of the formula to increase the crosslinking density and improve elasticity and resilience.
6. Why does silicone feel more “premium”?
Since silicone products are sprayed with a tactile oil, they have a soft, delicate feel, resist dusting, and are ergonomically friendly.
Summary
Understanding the differences and advantages between the two and integrating them with actual customer needs can provide precise support for product design and brand marketing strategies, helping companies achieve technological breakthroughs and commercial success. While both elastomers and silicones belong to the same elastic material category, elastomers are a broad category, with silicones offering the highest performance. However, differences in physical structure, chemical composition, and performance lead to significant differences in their applicable applications, costs, and processing techniques. Silicone, with its excellent heat resistance, environmental friendliness, and safety, has become the preferred choice in high-end applications, such as medical, baby products, kitchenware, and aviation. Elastomers, on the other hand, continue to dominate industrial manufacturing and traditional applications due to their versatility and cost advantages, and are suitable for consumer electronics, sports, and toys.
When selecting materials, customers should consider product positioning, application environment, certification requirements, and cost budget.
When seeking safety, durability, and a high-end experience, choose silicone; when focusing on cost and production efficiency, choose other elastomers.
If you need material selection, material parameter comparison, application cases and customized solutions, please contact Z.S.R. Our expert team will provide you with one-on-one technical and market consulting services.
Further Reading
Technical Related
About Author: Z.S.R International Group
Z.S.R International Group(Hong Kong) co., Limited, is a one-stop supplier for molded silicone products and silicone products molding solution provider in the consumer products field. We offer OEM services from silicone product design to Silicone products contract manufacturing. We have the capability for custom silicone tooling, LSR(Liquid silicone Rubber) molded silicone products, solid silicone molded products, molded silicone multi-colored products. We also can custom molded silicone, custom molded LSR, custom molded dripping injection dispensing(co-injection) silicone multi-colored products.