Why Doesn’t Silicone Melt Or Burn?
As a high-performance elastomer, silicone rubber is widely used in the medical, kitchenware, seals, maternal and child products and other industries. The topics of “silicone melting temperature” and “why silicone does not burn” are becoming increasingly popular. This article will analyze the causes and actual temperature performance from a professional perspective to help engineers, designers and purchasers scientifically select appropriate materials.
What is Silicone?
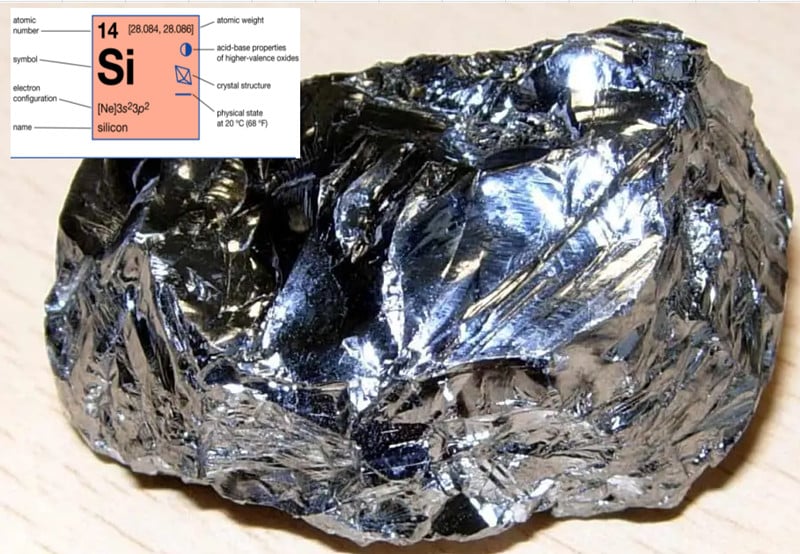
Silicones, also known as polysiloxanes, are polymers that include any synthetic compound made up of repeating units of siloxane, which is a chain of alternating silicon atoms and oxygen atoms, combined with carbon, hydrogen, and sometimes other elements.
They are typically heat-resistant and either liquid or rubber-like, and are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, and thermal and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, silicone grease, silicone rubber, silicone resin, and silicone caulk.
Silicone rubber offers good resistance to extreme temperatures, being able to operate normally from −100 to 350 °C (−148 to 662 °F). Some properties such as elongation, creep, cyclic flexing, tear strength, compression set, dielectric strength (at high voltage), thermal conductivity, fire resistance and in some cases tensile strength can be—at extreme temperatures—far superior to organic rubbers in general, although a few of these properties are still lower than for some specialty materials.
Silicone rubber is a material of choice in the industry when retention of initial shape and mechanical strength are desired under heavy thermal stress or sub-zero temperatures.
Organic rubber has a carbon-to-carbon backbone which can leave it susceptible to ozone, UV, heat and other aging factors that silicone rubber can withstand well. This makes silicone rubber one of the elastomers of choice in many extreme environments.
There are many special grades and forms of silicone rubber, including steam resistant, metal detectable, high tear strength, extremely high temperature, extremely low temperature, electrically conductive, chemical/oil/acid/gas resistant, low smoke emitting, and flame-retardant. A variety of fillers can be used in silicone rubber, although most are non-reinforcing and lower the tensile strength.
silicone safety concerns
1. Does Silicone melt?
Silicone does not have a traditional melting point
It is a thermosetting rubber with a cross-linked structure.
It will not melt above 200°C, but will gradually decompose.
The decomposition temperature range is about 200–350°C. Special formulas such as fluorosilicone can withstand up to 350°C, and extremes can reach 400°C.
Harsh combustion conditions and good self-extinguishing properties
It is not easy to ignite when the standard ambient temperature is <250°C. Even if it is exposed for a long time above 400°C, it will only decompose, carbonize or self-extinguish;
The combustion products are mainly white silica powder, which continues to burn without open flames.
While most plastics will begin to melt at high temperatures, silicone does not have a melting point and remains solid until combustion occurs.
Silicone doesn’t melt at quite high temperatures, but it does melt. so let’s explain by taking a second, deeper look at the naturally occurring chemical element silicon from which silicone rubber is made.
With the high temperature, When silicone decomposes, it becomes silicon. Then it will melt in 1414°C,so the silicon melting point is 1414 °C. The silicone does not melt in the oven as the oven will not get so high temperature. It does not melt in common used.
The first thing you will notice is that silicone doesn’t melt due to temperature alone! Special grades are available to further increase silicones already naturally high resistance to heat such as our silicone grade which can be used intermittently at temperatures up to 350°C
The applicable temperature range of silicone products, the temperature resistance range of conventional silica gel is -40℃~230℃,
The Silicon (no “e”) is a semimetallic element that melts at1414 °C, 2577°F.
After special treatment, the temperature resistance range of certain types of silicone products can be expanded to -110℃~350℃. So the silicone ice cube trays oven safe also if it made by Food Grade silicone.
In a low-temperature environment, the silicone product will become brittle if it exceeds the limit temperature that the silicone product can withstand.
In a high-temperature environment, if the temperature exceeds the limit temperature of 400℃, It will slowly lose its mechanical properties over time with extended high temperatures and then become brittle. The silicone products are carbonized.
When the temperature reaches about 600°C, the silica gel products will re-sulfurize, and the products will be sticky, like clay.
Without going into specifics silicone rubbers are known to remain stable at relatively high temperatures compared to most elastomer materials. Various silicone rubbers can be formulated, with additives, to withstand higher temperatures than the rubber alone can handle. Silicone (an adhesive compound of synthetic rubber) does not melt, Silicone rubbers do not melt but decompose when the temperature goes above certain limits. One of the decomposition products is silicon dioxide, also known as silicon.
2. Does Silicone burn?
Silicone is a non-flammable material in our lives. It is not easy to be burnt in an easy way. It would not burn if the temperature is 350℃. We always say silicone would not burn because the temperature of our lives would not be higher than 100℃. If the temperature is close to 430℃, the silicone would be burnt. But it would self-extinguish if it gets away from fire. So the silicone can be burn.
After the silicone burning. The burning area will become white. That is a way to check if your silicone products are real silicone made.
Learn More About Silicone Molding Method And Process
Why is silicone resistant to high temperatures and non-flammable?
Strong Si-O chemical bonds form the main chain, which has extremely strong thermal stability.
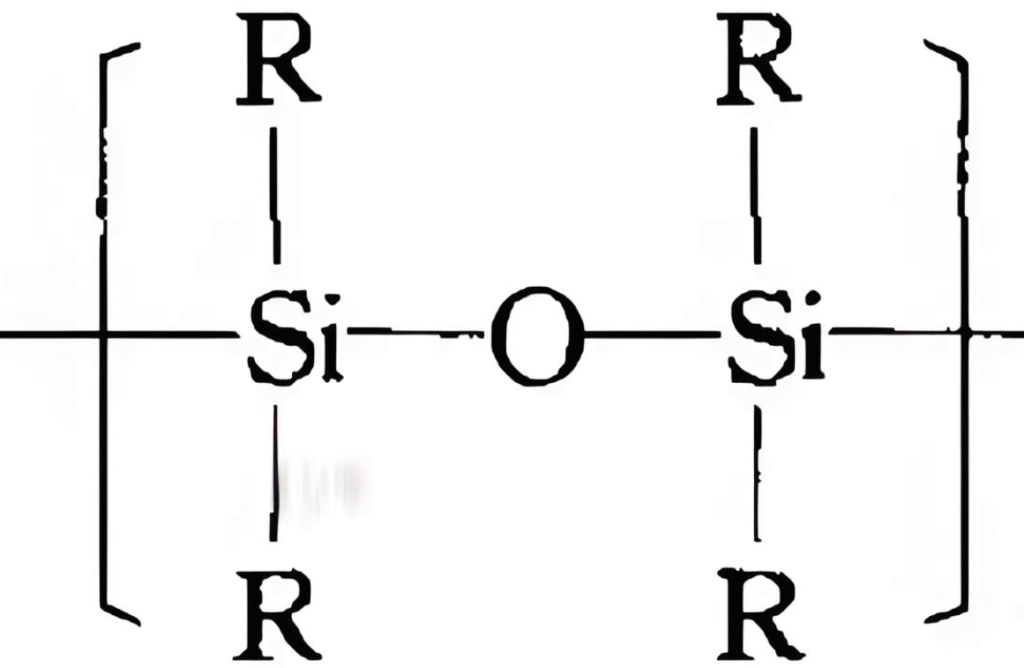
The molecular chains are cross-linked to form a thermosetting structure, which is not thermoplastic.
It is converted into silicon dioxide when burned, which is easy to extinguish and releases less smoke.
Why you care about the melting point and combustion characteristics of silicone?
If you are a material engineer/process developer: thermal limits and safety must be considered in material selection and processing; or if you are a product manager/purchaser: you need to understand the material limits for kitchenware, medical treatment, high-temperature sealing, etc.; your products need to be confirmed to comply with UL, V 0 or industry flame retardant standards.In order to keep the project and products safety, you may care about the silicone melting point.
When you need to keep them as the important ?
When you need your Mold thermal aging test: determine the decomposition and durability limits;
When you need use your products in high temperature environments: such as ovens, industrial heating pipes, etc.;
When you products need Fire safety assessment: flammability judgment in public facilities, electronic equipment and other scenarios.
When you products in Medical and laboratory equipment: high temperature sterilization (>200°C);
When you are an Kitchenware and baking supplies: need to withstand ovens of 200–260°C;
If your products is for electronic seals and aviation components: ensure heat and flame resistance;
How to verify and evaluate the thermal properties of silicone?
After the silicone raw material supplier offer the material technical data (TDS/MSDS), pay attention to “decomposition temperature” and “continuous use temperature”;
When you products finished,carry out high temperature aging and combustion tests to monitor performance changes;
Check whether the product has V 0 grade certification or UL 94 and other fire protection standards with SGS or other third parties.
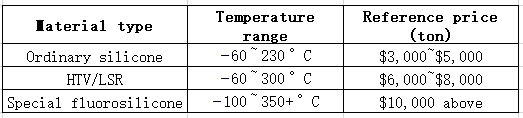
How much of cost with differnet silicone grade?
We also cancustomized formulas such as adding flame retardants and pigments will also affect costs.
More FAQ about silicone melting and burn
Q1: Can I use a hot air gun to defoam silicone molds?
A: Yes, hot air can be used at a long distance for a short time, and it will not melt
Q2: Will silicone soften under high temperature in the oven?
A: No, general food grade can withstand 230–250°C, high temperature grade can reach 300°C, and the actual measurement is stable
Q3: Why does silicone not melt but carbonize?
A: Above high temperature, the silicon oxygen structure breaks, leaving SiO₂ white powder, which is self-extinguishing
Q4: Why is silicone not a flammable material?
A: After burning out, only silicate remains, which will not continue to support combustion and is a flame retardant material
Q5: Will continuous high temperature damage performance?
A: Yes, it will gradually harden at 300°C for a long time. It is recommended to use it intermittently and replace it regularly.
Conclusion
From the above information, we can see that silicone can be melted or burned in special conditions.
Silicone does not melt like plastic, but decomposes at high temperatures due to its cross-linked structure; it has a high ignition point and self-extinguishes quickly, and the combustion products are mostly silicon dioxide, showing its superior thermal stability and flame retardancy. In fields such as kitchenware, seals, medical protection, and electronic aviation, these characteristics have become core elements in material selection and design.
In ZSR Group, We have rich experience in producing Custom silicone products with FDA or LFGB Approved standard products. We have the FDA register list number is 3011147430.
Any Silicone products or Silicone projects need technical support, contact us.
You also can customize Silicone products at ZSR Group.
Technical Related
About Author: Z.S.R International Group
Z.S.R International Group(Hong Kong) co., Limited, is a one-stop supplier for molded silicone products and silicone products molding solution provider in the consumer products field. We offer OEM services from silicone product design to Silicone products contract manufacturing. We have the capability for custom silicone tooling, LSR(Liquid silicone Rubber) molded silicone products, solid silicone molded products, molded silicone multi-colored products. We also can custom molded silicone, custom molded LSR, custom molded dripping injection dispensing(co-injection) silicone multi-colored products.



