Silicone rubber vs. Rubber: How to Choose Between These Two Elastic Materials?
Material selection is crucial in areas such as consumer electronics, automotive seals, kitchenware, and medical equipment. Although both silicone rubber and rubber are elastomers, they differ significantly in terms of high and low temperature resistance, chemical stability, processing methods, and service life. This article offers comprehensive insights into product compatibility, cost, and market strategy, providing a scientific basis for material selection for your product projects, helping you choose the right material based on your specific needs.
What is silicone rubber?
Silicone rubber : Organic silicone rubber materials are polysiloxane compounds with a siloxane (Si-O-Si) bond as their backbone. They are a type of organosilicon compound, containing at least one organic group directly attached to a silicon atom in their molecular structure.
These thermosetting elastic materials, with siloxane bonds as their backbone, are primarily used in products such as silicone rubber and silicone resins. They offer an extremely wide temperature range (-120°C to +300°C), a stable structure, and high biological inertness.
Ordinary silicone rubber is primarily composed of siloxane chains containing methyl groups and a small amount of vinyl groups. The introduction of phenyl groups improves silicone rubber’s high and low temperature resistance, while the introduction of trifluoropropyl and cyano groups enhances its heat and oil resistance. Silicone rubber exhibits excellent low-temperature resistance, generally remaining operational at -55°C. The introduction of phenyl groups increases this resistance to temperatures as low as -73°C. Silicone rubber also exhibits outstanding heat resistance, operating for extended periods at 180°C and maintaining elasticity for weeks or longer at temperatures slightly above 200°C. It can also withstand transient temperatures exceeding 300°C.

Silicone rubber has excellent breathability and the highest oxygen permeability among synthetic polymers. Furthermore, silicone rubber is physiologically inert and non-clotting, making it widely used in the medical field.
Silicone rubber is categorized into heat-vulcanized (high-temperature vulcanized silicone HTV) and room-temperature vulcanized (RTV) types. RTV types are further divided into polycondensation and addition reaction types. High-temperature silicone rubber is primarily used in the manufacture of various silicone rubber products, while room-temperature silicone rubber is primarily used as an adhesive, potting material, or mold. Heat-vulcanized silicone rubber is the most widely used type and is further categorized into methyl silicone rubber (MQ), methyl vinyl silicone rubber (VMQ, which is the most widely used and has the largest product range), and methyl vinyl phenyl silicone rubber (PVMQ) (which is resistant to low temperatures and radiation). Other types include nitrile silicone rubber and fluorosilicone rubber.
What is Rubber?
Rubber, including natural rubber and various synthetic rubbers (such as NBR, EPDM, styrene-butadiene rubber, chloroprene rubber, etc.), is mainly composed of carbon chain structures. Its elasticity comes from the expansion and contraction properties of the uncrosslinked chains. Rubber material is a highly elastic polymer material that can produce large deformations under external forces at room temperature and can quickly return to its original shape after the external force is removed. It is widely used in industrial products such as tires, seals, conveyor belts, cables, as well as in medical and electronic fields.

Why is it important to understand the difference between silicone rubber and rubber?
The core differences between silicone rubber and conventional rubber lie primarily in four key areas: composition, heat resistance, chemical stability, and application areas. Silicone rubber’s backbone is composed of silicon-oxygen bonds, offering superior high and low temperature resistance (-100°C to 350°C) and environmental safety. Conventional rubber, with its carbon-carbon backbone, offers advantages in oil resistance, flexibility, and cost control. Understanding the differences between the two can help you select the most suitable material for your project, ensuring its success.
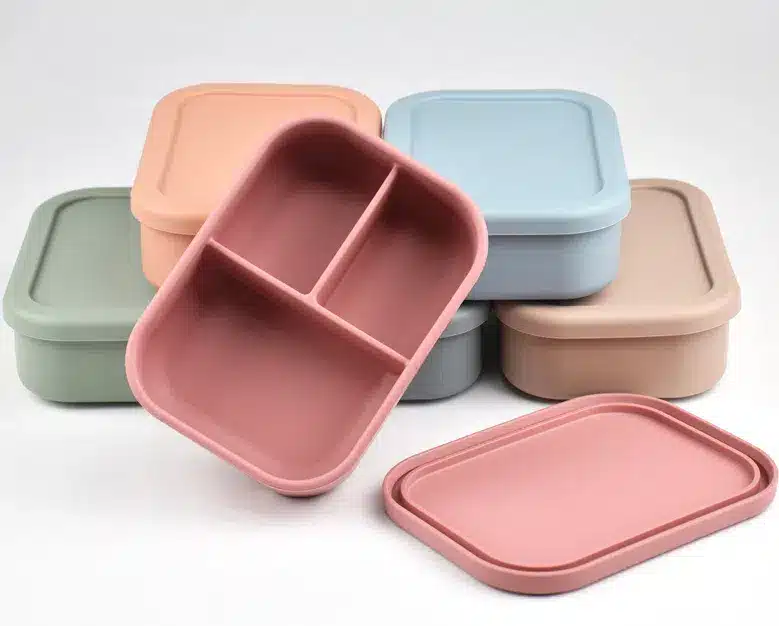

Based on the above characteristics, silicone rubber can be categorized as follows:
- Preferred Applications for Silicone Rubber:
- Medical: Prosthetic heart valves, high-temperature sterilizable instruments (high biocompatibility).
- Food Contact: Baby pacifiers, baking molds (FDA food-grade certified).
- Extreme Environments: Spacecraft seals, automotive spark plug boots (withstands extreme temperature fluctuations).

- Advantages of General Rubber:
- Industrial Seals: Chemical equipment oil seals, fuel lines (excellent oil resistance).
- Everyday Uses: Tires, shock absorbers (balanced high elasticity and abrasion resistance).
- Cost-Sensitive Applications: General Seals, Industrial Hose (30%-50% lower price).

Who cares about Silicone rubber vs. Rubber?
When to choose silicone rubber?
Extreme high/low temperature environments: exceeding 100°C or below -30°C. Silicone rubber has a wide temperature resistance range (-50°C to 200°C), making it particularly suitable for high-temperature environments. For example, medical catheters require high-temperature-resistant silicone rubber to ensure stability during sterilization.
For direct human contact or medical applications (such as catheters and impression materials), medical-grade silicone rubber should be selected. It must be certified to ISO 10993 and other standards to ensure sterility and biocompatibility. For food products that require non-toxicity and odorlessness, silicone rubber is recommended.
For weather resistance, long-term outdoor exposure, UV resistance, aging resistance, etc., silicone rubber is recommended.

When is rubber suitable for use?
Elasticity Requirements
When a material requires high elasticity to accommodate deformation or cushioning needs, such as in tires and shock absorbers.
Abrasion Resistance Requirements
In environments subject to frequent friction or prolonged use (such as conveyor belts, seals, belts, and high-pressure contact areas), rubber’s abrasion resistance can reduce wear and material loss.
Chemical Resistance Requirements
If the environment is exposed to oil, acids, alkalis, or high temperatures (such as in automotive fuel systems and chemical pipelines), highly chemically resistant materials such as nitrile rubber and fluororubber are more suitable.
Low-Temperature Environments
For environments below -50°C, EPDM or silicone rubber should be used to ensure low-temperature flexibility.

Where use the silicone rubber material?
1. Seals:
Silicone rubber has excellent heat and corrosion resistance and is widely used in the manufacture of seals such as rubber gaskets, sealing rings, and O-rings.
It can maintain its sealing properties in high-temperature environments and withstand corrosion from various chemicals.

2. Electronics and Electrical Industry: Silicone rubber is widely used in the electronics and electrical industry, for example, as insulation for cables and wires, encapsulation for electronic components, and as electronic sealants and gaskets.
3. Medical Devices:
Silicone rubber is heat-resistant and chemically stable, does not cause allergic reactions, and is easy to clean and sterilize.
Therefore, it is widely used in medical devices such as surgical instruments, catheters, and artificial organs.

4. Food Processing Industry: Silicone rubber meets food hygiene standards and can be used in direct food contact. It is commonly used in food troughs, sealing rings, and baking molds.
5. Construction Engineering: Silicone rubber has excellent weather and aging resistance and is widely used in construction projects for sealing, waterproofing, soundproofing, and outdoor seals.
6. Automotive Manufacturing: Silicone rubber is widely used in the automotive industry, such as in automotive seals, pipe connectors, and suspension systems.

7. Infant and child products: Because safety and non-toxicity are more stringent, silicone rubber is also widely used in the maternity and infant industry, including pacifiers, breast pump accessories, bowls and plates, and placemats.
Where use the rubber material?
Transportation
Natural rubber is primarily used in tire manufacturing (approximately 70% of global natural rubber is used for this purpose). It is also widely used in automotive seals, shock absorbers, and other components to reduce driving vibration and noise.
Industrial
Rubber is used in seals, conveyor belts, and shock absorbers. For example, rubber seals prevent fluid leakage, oil seals, mechanical seals, and anti-slip mats. Screens and liners made of wear-resistant rubber are suitable for mining equipment and have a service life of up to eight times that of ordinary rubber products.
Medical
Medical rubber products, including gloves, catheters, and stoppers, must meet strict hygiene standards and exhibit good biocompatibility to avoid harm to patients.
Daily Life
Rubber products are used in shoe soles, rain gear, toys, and other applications, providing wear resistance and safety.
How to choose silicone rubber or rubber?
The choice between silicone rubber and rubber should be determined based on the specific application’s requirements for temperature resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength.
Heat Resistance
Silicone rubber has a wider temperature range. Ordinary silicone rubber can withstand temperatures from -60°C to 250°C, while high-temperature silicone rubber can withstand temperatures exceeding 300°C for short periods. Rubber is generally stable between -30°C and 100°C, and tends to harden or soften outside this range.
Evaluate the application temperature and environmental factors of the project product: silicone rubber is preferred in extreme environments.

Chemical Stability
Silicone rubber is stable to most acidic and alkaline solutions, with the exception of strong alkalis and hydrofluoric acid. Among rubbers, fluororubber offers strong corrosion resistance, but may still swell and fail in strong acids.
Mechanical Strength and Elasticity
Rubber offers greater elasticity (a rebound rate of over 85%) and excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for shock absorption and anti-slip applications. Silicone rubber has weak tear resistance and can be easily permanently deformed by sharp objects. Clarify mechanical strength and wear resistance requirements: rubber is preferred for applications with high wear.
Aging and Maintenance
Rubber is susceptible to UV rays and requires inspection and replacement every two years for outdoor use. Normal oxidation of silicone rubber can be restored with toothpaste, but avoid rubbing with alcohol. Cost and Processing
Food-grade silicone rubber raw materials cost 3-5 times more than natural rubber and require specialized equipment for molding. Rubber is simple to process, using traditional vulcanization techniques. It is also recyclable and environmentally friendly. However, considering safety and regulatory compliance, silicone rubber is more suitable for food or medical applications.
Finally, first-run samples can be tested for thermal aging, tensile strength, compression rebound, and chemical exposure to further refine the material selection process.
Cost and price/performance ratio
The cost and cost-effectiveness of silicone rubber and rubber need to be determined based on the specific application scenario:
Cost comparison
Silicone rubber: The raw material price is relatively high (approximately 30-60 yuan/kg), but the material utilization rate is high, and no waste is generated during processing.
Rubber: The raw material cost is relatively low (approximately 10-30 yuan/kg), but there may be 5-10% loss during mixing, and manual trimming and post-processing are required.
The price is about 1.5-2 times that of rubber, but the service life is long (about four times) and maintenance is low.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Mass Production: Rubber molds are more suitable for low-cost applications due to their low cost and fast processing, making them ideal for high-volume and cost-sensitive projects.
Mass Production: Silicone rubber offers a lower overall cost due to its high degree of automation and low labor costs.
Complex Structure Products: Silicone rubber offers high precision and flash-free manufacturing, making it suitable for precision manufacturing; rubber struggles to meet high-precision requirements.

Heat Resistance: Silicone rubber ‘s temperature resistance range (-60°C to 250°C) far exceeds that of rubber (-30°C to 100°C), but rubber is more stable at low temperatures.
How to Produce silicone rubber products VS rubber products?
Silicone rubber is suitable for small-batch customization or products with high requirements for temperature resistance, safety, and environmental protection; rubber is suitable for large-volume, function-oriented products.
How to Control silicone rubber products quality?
- Raw material inspection and review: Check hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, and tear strength; review raw material certification (FDA/LFGB);
- Mold production and control: Mold precision control to avoid burrs and flash;
- Mass production testing and random inspections to ensure batch stability and avoid defects such as color difference, bubbles, and raw rubber.

How to Control rubber products quality?
Key areas of quality control for rubber products include raw material management, production process control, and finished product testing.
Raw Material Management
Supplier qualifications (e.g., ISO certification and supply capacity) must be strictly screened. Raw materials must be tested for harmful substances and physical properties (e.g., tensile strength and elastic modulus) to avoid using raw materials with high impurity content.
Production Process Control
- Formulation and Process Parameters: Precisely control the vulcanization temperature, time, and order of compounding agent addition to avoid uneven mixing or under/over-vulcanization. Ensure a stable vulcanization process (vulcanization time and temperature) to prevent scorching and mold release difficulties during processing. Accurate filler ratios are required to prevent cracking and aging.
- Optimize mold design to avoid edge removal difficulties or dimensional deviations.
- Equipment Maintenance: Regularly calibrate equipment parameters such as mixers and calenders to ensure operational accuracy.
Finished Product Testing
Focus on testing performance indicators such as tensile strength, tear strength, and hardness to ensure product compliance with safety standards (e.g., GB 4806.11-2023).
How to Clean Silicone rubber and Rubber Products?
For silicone rubber products, we generally choose warm water + neutral detergent, or high temperature disinfection, avoid strong acid and alkali cleaning.
For rubber products, we usually choose to wipe with a damp cloth or a weak alkaline detergent. Do not heat at high temperatures to avoid hardening/aging.

More FAQs
Summary
Silicone rubber and rubber aren’t about which is better. Material selection depends on application requirements, cost budget, environmental conditions, safety level, and physical properties.
Rubber: Optimizing cost and wear resistance, rubber is more suitable for industrial-grade, oil-resistant, pressure-resistant, and structurally functional applications, as well as for cost-effective and durable products.
Silicone rubber: Resistant to extreme environments, non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and safe, it’s suitable for high-temperature, medical, and child-friendly applications, as well as for aesthetically pleasing and outdoor applications.
“Silicone rubber is the preferred choice for extreme environments and food/medical safety. Rubber is the preferred choice for cost-effectiveness and recycling advantages. If both are required, a material combination strategy can be adopted to enhance product competitiveness.” If you have a project requiring material selection, please contact Z.S.R for professional advice to help you achieve your project goals as quickly as possible.
Further Reading
Technical Related
About Author: Z.S.R International Group
Z.S.R International Group(Hong Kong) co., Limited, is a one-stop supplier for molded silicone products and silicone products molding solution provider in the consumer products field. We offer OEM services from silicone product design to Silicone products contract manufacturing. We have the capability for custom silicone tooling, LSR(Liquid silicone Rubber) molded silicone products, solid silicone molded products, molded silicone multi-colored products. We also can custom molded silicone, custom molded LSR, custom molded dripping injection dispensing(co-injection) silicone multi-colored products.