Silicone Rubber VS EPDM
Silicone rubber and EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer Rubber) are both elastomers widely used in the automotive, construction, electronics, appliance, food and medical, and consumer goods industries. However, due to their different molecular structures, they exhibit significant differences in temperature resistance, aging resistance, chemical resistance, flexibility, and application areas. They are often compared and selected side by side.
Which is better suited for high-temperature environments?
Which is more resistant to ozone and UV rays?
Is there a significant cost difference?
For food contact products, which meets FDA or EU standards?
Should I use silicone or EPDM?
This article systematically compares silicone rubber and EPDM to help engineers, buyers, brands, and entrepreneurs make the right decision.
What are Silicone Rubber VS EPDM?
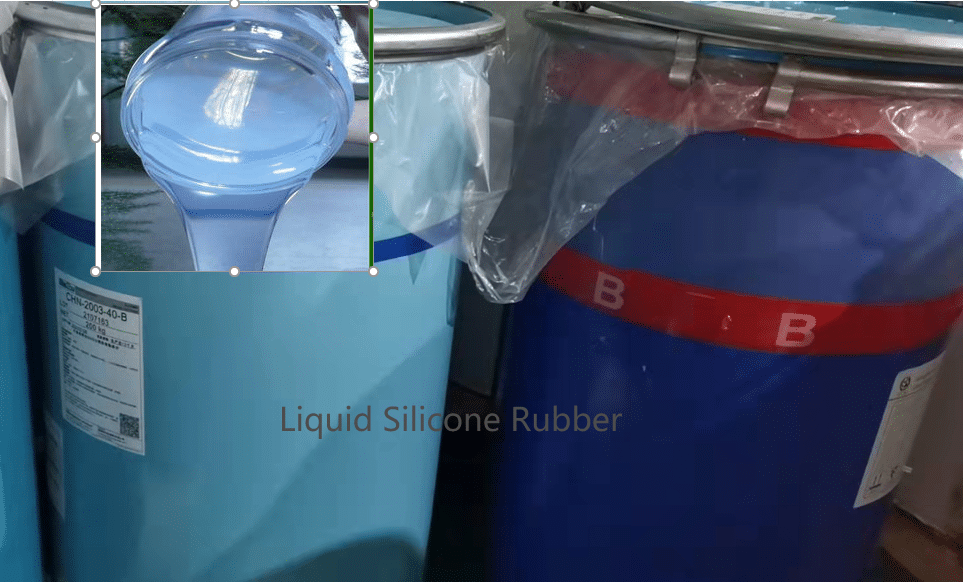
Silicone Rubber (Silicone): Composed of a polysiloxane backbone with fillers and crosslinkers, it has a Si–O–Si backbone structure and is available in various grades, including HTV (High Temperature Vulcanized), LSR (Liquid Silicone Rubber), and RTV (Room Temperature Vulcanized). It offers excellent high and low temperature resistance (-60°C to +250°C) and high physiological inertness. It is widely used in baby products, food, medical devices, and automotive high-temperature seals.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): Made by copolymerizing ethylene, propylene, and a tertiary monomer (such as Diene), it is a synthetic rubber with a saturated chain structure. It is primarily used in roof waterproofing, door and window seals, automotive cooling water pipes, automotive sealing strips, and roof waterproofing membranes. It exhibits excellent ozone, weathering, and aging resistance.
Why compare Silicone Rubber VS EPDM?
Because both are commonly used in seals, gaskets, piping, and consumer products, but their performance and cost differ significantly, understanding the differences between the two is crucial for project material selection and client application decisions.
Silicone:
EPDM:
However, EPDM is easily damaged by oil, fuel, and non-polar organic solvents, making it unsuitable for use in oil-based environments.
Choosing the wrong material during the project design phase can result in costly waste or product failure.
Who is interested in the difference of Silicone Rubber and EPDM?
R&D engineers at brands or manufacturers need to select materials. When products require high-temperature, food-contact, or medical-grade materials, silicone is the preferred choice. When products require weather resistance, UV resistance, and low-cost, high-volume production, EPDM is the preferred choice. In mixed applications (such as automotive parts), silicone and EPDM may be used in some applications.
Purchasing managers at accessory users: They prioritize cost and supply stability. When low cost is a priority, EPDM is the preferred choice.
Consumer product brands and entrepreneurs: They need to balance safety certifications with market positioning. Silicone is the preferred choice for pacifiers, kitchenware, medical catheters, electronic seals, and wearables. EPDM is the preferred choice for automotive door and window seals, roofing membranes, industrial pipe seals, and construction sealants.
Building material suppliers and maintenance personnel: EPDM is a material that is sensitive to outdoor seals and roof membranes. It is suitable for long-term exposure environments, such as building roof waterproofing, automotive door seals, and HVAC system seals.
Automotive OEM buyers and engineers: They focus on seals’ oil resistance, high temperature resistance, and weather resistance. It is suitable for high-temperature sealing, food contact, medical devices, and high-temperature electronic interfaces.
Industrial manufacturers: They focus on balancing cost, durability, and performance. EPDM is primarily used in outdoor, medium-temperature, and dynamic friction environments. Silicone is used for high-temperature and low-temperature sealing, as well as for food-grade and specialized industrial applications.
End users: When safety and user experience are important, silicone is the preferred choice. When durability and cost are important, EPDM is the preferred choice.
Z.S.R’s team work with the different industries brand’s Owners, products development managers, products managers, products designers together and offer them OEM ODM solution from molded silicone products design, prototyping to silicone products contract manufacturing, printing, package to ensure their silicone projects success.

Custom Silicone Products | OEM/ODM Service
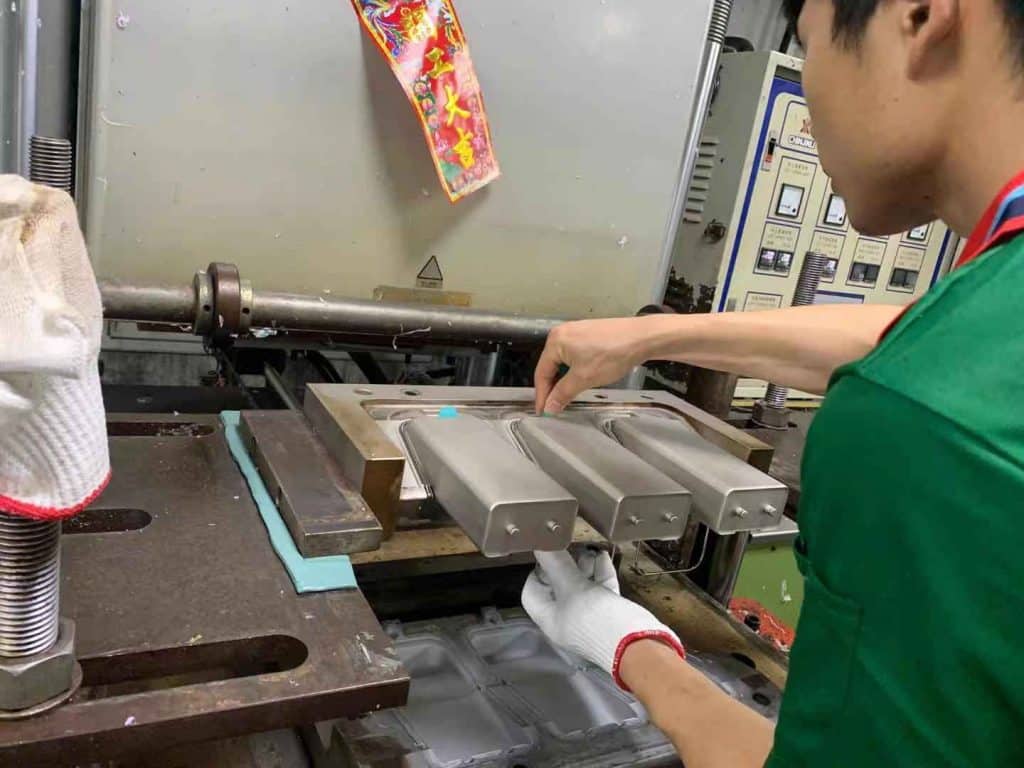
How to produce silicone products?
Silicone product production primarily utilizes three core processes: compression molding, injection molding, and extrusion. These processes are complemented by raw material preparation, vulcanization, and post-processing.
Basic Production Process
Raw Material Preparation:
Silicone rubber is primarily used, with auxiliary materials such as a vulcanizing agent (such as peroxide), color paste (Pantone color palette), and a catalyst added. The mixture is then mixed uniformly in a rubber mixer.
Molding Process:
Compression molding: Solid silicone rubber is cut and placed into a steel mold. Vulcanization is performed in a vulcanizer at 150-180°C and 10-20 MPa pressure for 3-15 minutes. This process is suitable for simple structural products such as seals and buttons.
Injection molding: Liquid silicone is mixed in an injection molding machine, injected into a mold, and rapidly vulcanized at low temperatures of 120-160°C. The resulting product achieves an accuracy of ±0.05mm and is used for delicate parts such as baby pacifiers and medical catheters.
Extrusion Molding: Silicone is extruded into tubes or sheets using a screw, then cured in a vulcanizer using microwaves or hot air before being cut. Suitable for continuous products such as silicone tubing and sealing strips.
Post-processing: This includes trimming and deburring (manual or freeze-dried), secondary vulcanization (baking at 200°C for 2 hours to remove odor), surface treatment (spraying, laser engraving), and hardness and dimensional testing.
Key Materials and Equipment
Core Materials:
Silicone rubber (solid or liquid), bis(2,4-dimethyl-2,5-dioxane) vulcanizing agents, fumed silica (reinforcement agent), and silicone oil (for flowability adjustment).
Main Equipment:
Compression vulcanizing press (20-200 tons pressure).
Liquid silicone injection molding machine (equipped with precision screw).
Vacuum rubber mixer (mixing uniformity >98%).
Microwave continuous vulcanization line (speed 5-30 m/min).
Z.S.R’s Precision Silicone mold /tooling ,Silicone Compression molding(42sets), Silicone over-molding, Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection molding: LSR molding, Liquid silicone rubber overmolding, LSR Multi-Shot (LSR/Thermoplastic/Metal), silicone Dripping molding, capabilities allow us to manufacture any type silicone rubber products for your company’s needs in an infinite variety of design, function, material, structure, shape, sizes, color, logo, pattern, package, label configurations etc.
Key Process Control Points
Temperature Tolerance: The mold vulcanization temperature must be controlled within ±2°C. A temperature difference exceeding 5°C during injection molding can cause product warping.
Pressure Matching: Molding pressure is inversely proportional to product thickness. A 1mm thick product requires 15MPa, and the pressure decreases by 3MPa for every 1mm increase in thickness.
Time Control: Silicone vulcanization has a scorch period (approximately 3 minutes at 120°C). Mold filling must be completed before scorch occurs.
Z.S.R consists of a strong engineering design team 12 experts with more than 20 years’ experience. We offer personalized services and supports for projects through all steps of products development. From conceptual design, silicone material selection, engineering, prototyping and testing, to final volume production and assembly.
How to produce EPDM products?
The production process for EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) products varies depending on the product type. The following is an overview of the main production methods:
Waterproofing Membrane Production Process
Raw Material Preparation: Ethylene, propylene, and diene copolymers are primarily used, with polyolefin hot welding agents (such as DOP), carbon black, and accelerators added.
Continuous Vulcanization: The raw materials are mixed in a cold feed extruder and then continuously vulcanized (controlled at 250-280°C) to form sheets.
Welding: Hot air welding or adhesive bonding is used, with roller pressure applied to achieve effective welds 40-50mm wide.
Rubber Granule Production Process
Raw Material Processing: The raw rubber is heated and mixed in an internal mixer, then color-adjusted and pressed into long blocks.
Vulcanization Crushing: The raw rubber is placed in a vulcanizing tank and vulcanized. After vulcanization, the vulcanized rubber is crushed into granules and packaged by size.
Environmentally friendly features: A non-toxic formula with anti-fungal and antibacterial ingredients is used, ensuring easy maintenance (cleaning with water or a neutral detergent).
Hose Production Process
Raw Material Mixing: The raw rubber is mixed with compounding agents (such as vulcanizing agents and reinforcing fibers) until uniformly mixed.
Extrusion: The inner tube, reinforcement layer, and outer tube are produced using an extruder.
Vulcanization: Cross-linking and curing is performed using high temperature or radiation to form a three-dimensional network structure.
General Rubber Product Production
Massaging and Mixing: The raw rubber and compounding agents are uniformly mixed using an open mill or internal mixer.
Molding: Forming is performed using processes such as calendering and extrusion, or autoclave vulcanization is performed.
Post-Processing: Demolding, labeling, inspection, and packaging for shipment.
Different products require customized formulations and process parameters based on specific requirements. For example, waterproof membranes prioritize weldability, while rubber granules emphasize wear resistance and environmental friendliness.

How to choose Silicone rubber or EPDM material?
If the product requires high-temperature resistance (>150°C), oil resistance, food grade, and long-term flexibility, silicone is recommended.
If weather resistance, abrasion resistance, water resistance, or cost-sensitive applications are required, EPDM is preferred.
Silicone is preferred for food/medical applications; EPDM can be an option for industrial/automotive applications.
How to Control Silicone rubber products quality?
Silicone product quality control requires comprehensive control throughout the entire process, from raw materials and production processes to finished product testing. The following are key control points:
Raw Material Management
Supplier Audits: Select ISO-certified suppliers and regularly evaluate their quality management systems, production capabilities, and historical supply quality.
Raw Material Testing: Each batch of raw materials must be tested for appearance, physical properties (hardness, tensile strength), chemical properties (acid and alkali resistance, aging resistance), and microbiological indicators (for medical/food-grade silicone).
Storage Management: Warehouses must be dry, ventilated, and protected from light. A first-in, first-out (FIFO) principle must be implemented to ensure raw materials are used within their expiration date.
Production Process Optimization
Formula Design: Formulas are designed based on the application scenario, taking into account raw material compatibility, processing temperature, and curing time to ensure repeatability.
Molding Process: Injection molding requires precise control of pressure, speed, and temperature.
Compression molding requires optimized mold design, preheat temperature, and venting slot placement.
Post-Processing: This includes deburring, cleaning, drying, and post-curing treatment to enhance product durability and safety.
Quality Control and Testing
Online Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of production parameters (temperature, pressure, time) and product dimensions.
Finished Product Inspection: Dimensional accuracy, appearance quality, and bond strength are inspected using tools such as calipers and microscopes.
Environmental Control: Medical-grade production requires maintaining Class 10,000 cleanliness (ISO Class 7) and a humidity level of 40%-60%.

Special Scenarios Management
Medical-grade: Requires ISO 10993 biocompatibility testing, and raw materials must comply with FDA/LFGB certification.
Food-grade: Testing focuses on microbial contamination and chemical stability.
Z.S.R understand the importance of quality, our whole-process quality control system ensures that our customers can receive the qualified products as they approved before mass production.
How to Control EPDM products quality?
EPDM product quality control requires strict scrutiny from raw materials, production, and construction stages to ensure compliance with national standards and environmental protection requirements. The following are key control points:
Raw Material Quality Control
Environmental Indicators: EPDM granules must pass GB/T 14833-2020 testing, with soluble lead ≤ 30 mg/kg and no detection of 18 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs); polyurethane adhesive free TDI content ≤ 0.2%, TVOC emission ≤ 0.1 mg/m³ (72-hour closed-loop test).
Physical Properties: Particle size 0.5-3 mm, particle size pass rate ≥ 95%; adhesive solids content ≥ 65%, tensile bond strength ≥ 2.0 MPa.
Supplier Screening: Prioritize ISO 9001/14001 certified manufacturers. SGS test reports and MSDS safety data sheets for the same batch of products are required.
Production Process Monitoring
Factory Inspections: Verify the EPDM granule mixing temperature (150-170°C) and mixing time (≥15 minutes). Real-time monitoring of the pH value (6.5-8.5) and viscosity (3000-5000 cps) of the reactor in the glue production line.
Batch Management: Each batch of materials is marked with a unique traceability code. 10% of incoming materials are sampled, focusing on heavy metal migration and aging resistance.
Key Construction Controls
Environmental Conditions: Construction temperature 10-35°C, humidity ≤ 75%. Operations are strictly prohibited on rainy days or when the base moisture content exceeds 5%.
Process Specifications: Pavement thickness for breathable runways ≥ 8mm. PU base coat for hybrid runways must be applied in two separate passes, with an interval of ≥ 4 hours.
Process Recording: Daily records are kept of glue opening time, usage, and curing status. High-definition video footage is maintained at key milestones.
Acceptance and Maintenance
Environmental Re-inspection: Seven days after completion, sampling will be conducted using a 20m x 20m grid method to test for benzo[a]pyrene (≤0.1mg/kg) and short-chain chlorinated paraffins (SCCPs ≤0.1%).
Long-term Monitoring: Quarterly monitoring of surface hardness (Shore A durometer, standard value 45-60), and annual UV aging simulation testing (color difference ΔE ≤3).


How to Clean silicone rubber products or EPDM products?
- EPDM, avoid using strong solvents; use warm water and a neutral detergent.
- Silicone can be cleaned with warm water and a food detergent. High-temperature sterilization is permitted.
How much of the silicone rubber products or EPDM products?
Silicone: Raw material prices are relatively high ($3-6/kg), mold and production equipment costs are high, and overall prices are high due to complex processes and high certification costs.
EPDM raw material prices are generally around $2-4/kg; it is suitable for large-scale production and has a low overall cost.
More FAQs
Summary
While EPDM and Silicone Rubber share some similar properties, their application scenarios differ significantly:
If the application involves outdoor use, waterproofing, sportswear, automotive and construction applications, and requires temperatures below 150°C, EPDM is the more economical and durable choice.
If the product requires high-temperature resistance, flexible sealing, food/medical safety, and adaptability to extreme environments, silicone rubber is a better choice. Silicone rubber is also suitable for high-end consumer products and medical applications.
If your customer base prioritizes safety, certifications, and a high-end experience, choose silicone rubber.
If your customer base prioritizes cost, weather resistance, and volume production, choose EPDM.
The final material choice should be based on specific application requirements, budget, and user experience. Understanding the differences between the two materials will ensure you make the right investment, meeting technical specifications while enhancing your brand’s added value.
Z.S.R support our partner silicone products from idea to market. We are the partner of choice for leading silicone products brands and retailers. The silicone products what we made suitable for various industries, including consumer, industrial, medical. Recognized for delivering innovative custom-molded silicone products, manufacturing expertise, and technical solutions to them.
Contact Z.S.R experts to choose the fitted material for your projects.
Further Reading
Technical Related
About Author: Z.S.R International Group
Z.S.R International Group(Hong Kong) co., Limited, is a one-stop supplier for molded silicone products and silicone products molding solution provider in the consumer products field. We offer OEM services from silicone product design to Silicone products contract manufacturing. We have the capability for custom silicone tooling, LSR(Liquid silicone Rubber) molded silicone products, solid silicone molded products, molded silicone multi-colored products. We also can custom molded silicone, custom molded LSR, custom molded dripping injection dispensing(co-injection) silicone multi-colored products.