Silicon vs. TPU: Which is the best choice?
Silicone and TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) are the two most popular elastic materials used in mobile phone cases, wearable accessories, baby products, sports protective gear, and other fields. They each offer advantages in terms of softness, wear resistance, heat resistance, cost, and design. This article comprehensively compares these materials, covering aspects such as material performance, production compatibility, and user experience, to help brands, engineers, and consumers identify the optimal material solution.
What is SILICONE?
Silicone, refers to a polymeric organic compound primarily composed of polydimethylsiloxane.
It is an excellent high-temperature elastic material. Silicone is an organosilicon compound containing Si-C bonds and at least one organic group directly attached to a silicon atom. Compounds in which organic groups are attached to silicon atoms through oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen, or other molecules are also commonly considered organosilicon compounds. This polymeric silicone elastomer is soft, smooth, and resistant to extreme temperatures. It is not easily decomposed by UV light and ozone. Silicone possesses superior thermal stability, radiation resistance, and weathering resistance compared to other polymers.

What is TPU?
Thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer, also known as thermoplastic polyurethane rubber (TPU), is a (AB)n-type segmented linear polymer.
A is a high molecular weight (1000-6000) polyester or polyether, B is a diol with 2-12 linear carbon atoms, and the chemical structure between the AB segments is a diisocyanate. Thermoplastic polyurethane rubber is crosslinked by intermolecular hydrogen bonds or by light crosslinking between macromolecular chains. Both crosslinking structures are reversible with increasing or decreasing temperature. In the molten state or solution, intermolecular forces weaken.
However, upon cooling or solvent evaporation, strong intermolecular forces re-establish the bonds, restoring the original solid properties.

This material combines the elasticity of rubber with the processability of plastic, offering adjustable mechanical properties ranging from 60A to 80D Shore hardness. It is widely used in footwear, automotive seals, mobile phone cases, wire sheathing, and medical devices.
Why choose Silicone vs TPU?
The choice between silicone and TPU depends on specific needs. The two differ significantly in material properties and applicable scenarios.
TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) combines the elasticity of rubber with the processing properties of plastic. It offers a wide hardness range (Shore A 60-95), outstanding wear resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for applications requiring high elasticity and wear resistance.
Silicone, based on silicon-oxygen chains, offers a wider temperature resistance range (-60°C to 230°C) and exceptional chemical stability, making it suitable for extreme temperatures and complex chemical environments.
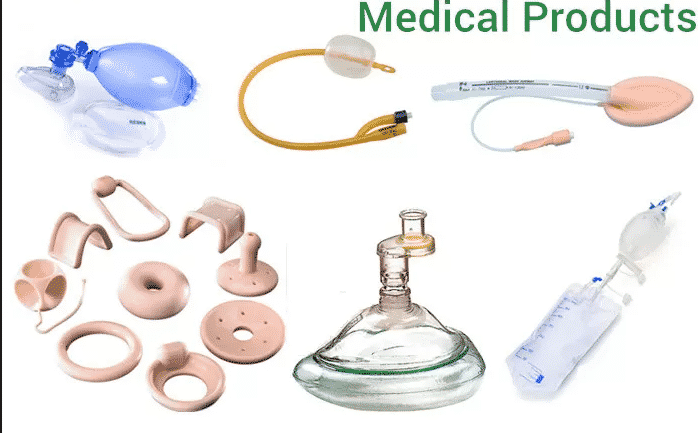
Applications: TPU is widely used in sports equipment, shoe soles, and automotive parts, where its high elasticity and wear resistance effectively withstand daily wear and tear. Silicone, on the other hand, is suitable for medical devices, kitchen utensils, and seals. Its high-temperature and UV resistance make it more stable in complex environments.

If you’re looking for high-quality, affordable custom silicone products, come to Z.S.R
Please take a look at the simple advantage comparison to make material selection faster:
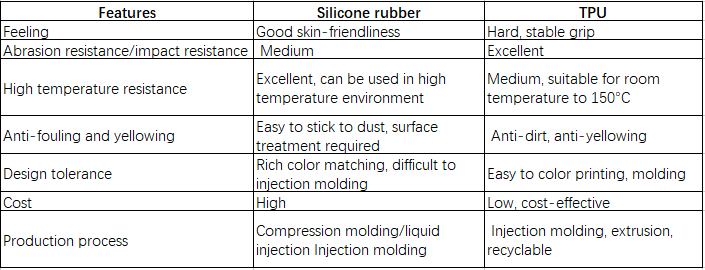
Who would choose to use silicone material and who would choose to use TPU material?
Generally speaking, for those prioritizing durability and cost control, we recommend TPU. For users who prefer a comfortable feel and softness, we recommend silicone. For equipment manufacturers and brand owners of these products, choose based on product positioning and functional scenarios. Silicone is recommended, especially for high-temperature applications and those prioritizing FDA certification requirements. For OEM/ODM account managers who are willing to balance cost and performance, TPU is preferred. For the maternal and infant/medical industries, silicone is recommended for applications requiring boiling resistance and high hygiene standards.

When should silicone be used? When should TPU be used?
When heat resistance, high temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, UV resistance, ozone and mold erosion resistance, boiling and strong disinfection are required, we recommend that customers choose silicone materials. Silicone materials are the first choice when extreme temperatures, outdoor weather resistance, medical implants, etc.

When emphasizing drop resistance, oil resistance, wear resistance, abrasion resistance, and structural protection, we recommend customers to use TPU materials. TPU materials are preferred for sports equipment, mobile phone protection, and wear-resistant products. At the same time, if the customer’s industry is budget-sensitive and does not require high temperature use, we recommend that the customer choose TPU.
Silicone is preferred for applications requiring high temperatures, chemical corrosion, medical safety, and electronic insulation, while TPU is preferred for applications requiring wear and oil resistance, lightweight processing, and long-term durability. While the two may overlap in practical applications (such as mobile phone cases), further differentiation can be made based on properties such as hardness and feel.


Where is silicone material used and where is TPU material used?
High temperature resistant environment:
Silicone has high temperature resistant properties and is suitable for scenarios that need to withstand high temperature or chemical corrosion, such as electronic appliances, new energy vehicles and other fields.

Skin-friendly and flexible requirements:
Silicone is soft and skin-friendly, non-toxic and odorless, and is suitable for humanoid robot skin, medical and other fields.
For example, silicone materials used in baby food molds, pacifiers, kitchen accessories, and electrical appliance seals;

Wear resistance and elasticity requirements: TPU is wear-resistant and has excellent elasticity, making it commonly used in sports equipment, toys, and industrial products.
High hardness and versatility: TPU has adjustable hardness and a variety of processing methods, making it suitable for consumer products such as mobile phone cases and tablet cases. Examples include mobile phone cases, 3C product casings, sports protective gear, outdoor equipment, and shoe soles.
How to produce silicone products?
Silicone :
Solid Silicone Compression Molding
The mixed silicone material is placed into a mold and vulcanized at high temperature. This process is suitable for high-precision, complex-shaped sealing components such as seals and buttons. Compression molding involves eight steps:
1. Raw Material Pretreatment
Solid silicone requires mixing: Mixing is done on an open mixer (temperature ≤ 45°C) to maintain a hardness fluctuation of ≤ ±2°.
Preforming and Cutting: Cut the rubber into pieces 1.1-1.2 times the mold cavity volume (to prevent material shortages and excessive flash).
2. Mold Pretreatment
Medical molds must be preheated to 160-180°C (120°C for standard molds).
Spray with food-grade release agent (0.5-1.5 mg/cm²; excessive application may cause surface grease stains).

3. Loading Positioning
Precisely weigh the rubber compound (error ≤ ±0.5%) to prevent uneven cavity pressure.
Case study: A urinary catheter leaked due to a 0.3g loading deviation, resulting in a 0.15mm difference in tube wall thickness.
4. Mold Closure and Pressurization
Initial Pressing: 5-10 MPa low-pressure venting (to prevent trapped air and bubbles);
High-Pressure Molding: 15-25 MPa holding pressure, time calculated based on thickness (60 seconds for 1 mm).
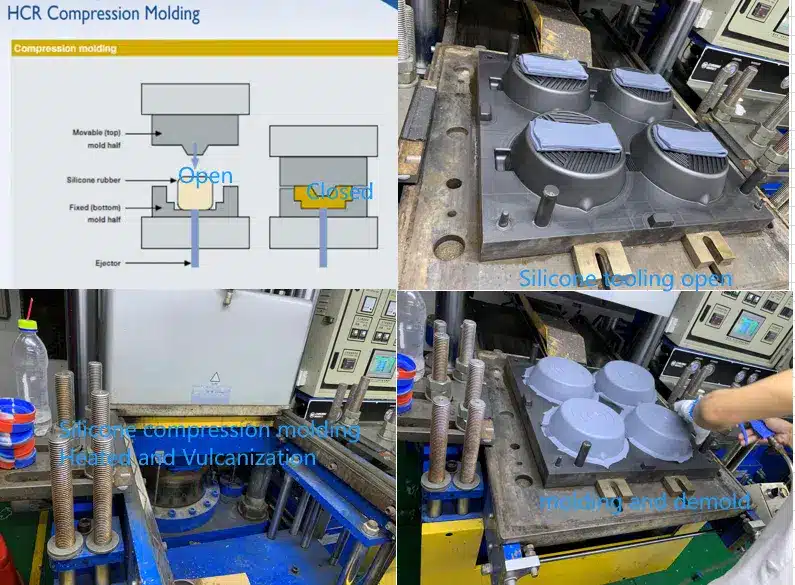
5. Vulcanization
Temperature Control: 170 ± 2°C (temperature fluctuations > 3°C will affect crosslinking);
Vulcanization Time = Thickest Part (mm) × 1.5 minutes (e.g., 7.5 minutes for 5 mm thickness).
6. Mold Opening and Part Removal
Medical products must be removed using a suction cup robot (no bare hands allowed).
Immediately place in a cooling fixture to set the shape (to prevent deformation from high temperatures).
7. Post-Processing
Flash Treatment: Medical parts require a cryo-deburring machine (-70°C brittle trimming).
Plasma Cleaning: Remove surface release agent residue (dyne value > 50 mN/m).
8. Full Packaging Inspection
100% dimensional inspection (projector accuracy ±0.005mm);
Particle control: Screening with a laser particle counter (particles >0.3μm, ≤100/cm²).

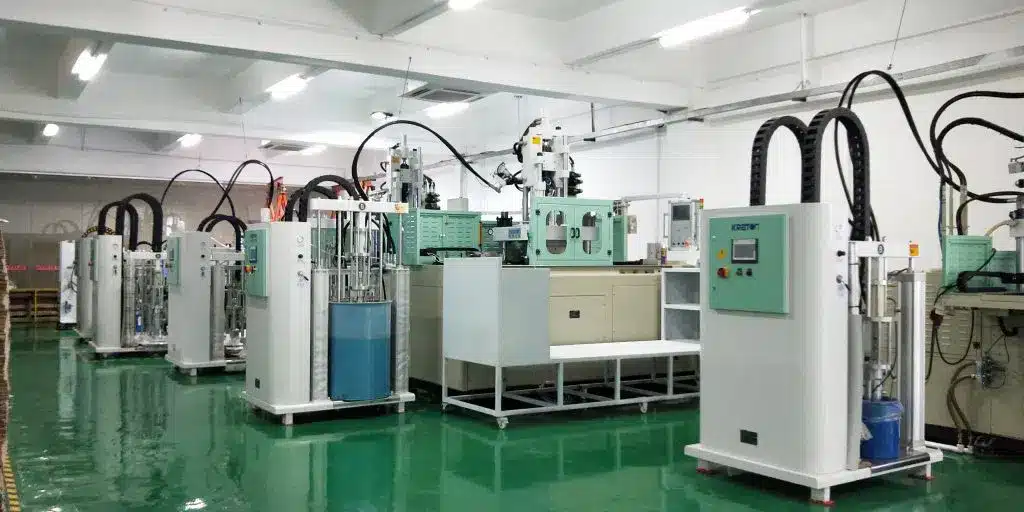
Liquid silicone injection molding
The heated silicone material is injected into the mold through an injection molding machine and then cooled to solidify.
It is suitable for products that require high flexibility, such as medical catheters and baby bottle nipples.

Liquid silicone selection and ratio: Select the appropriate liquid silicone type based on a comprehensive assessment of the product’s application, properties, and shape. Phase A silicone serves as the main material, while phase B silicone acts as the crosslinker, curing agent, and auxiliary agent. By controlling the ratio of components A and B, you can adjust the silicone’s curing speed, hardness, color, and other properties.
Mold design:
Mold design is a key step in the liquid silicone injection molding process.
Mold design must take into account factors such as product shape, size, wall thickness, surface requirements, and other factors to ensure good product performance.

Mixing and conveying of liquid silicone: The liquid silicone dosing system delivers phases A and B of liquid silicone in proportion, which are then mixed and appropriately colored at the mixing assembly. The mixed liquid silicone enters a static mixer through a pressure reducing valve and a check valve for homogenization, and then enters the injection molding machine’s metering pipe through a control valve.
Injection molding: The screw conveys the liquid silicone and further homogenizes it. When the liquid silicone reaches the front of the check valve, the check valve quickly closes for injection, and the screw pushes the liquid silicone through the switch nozzle and cold runner system into the mold cavity.
Curing and demolding:
Under high temperature and high pressure, the liquid silicone rapidly vulcanizes and cures within the mold cavity. Once the silicone is fully cured, the mold is opened and the product is removed. After demolding, the product undergoes a quality inspection, including appearance, dimensions, and performance.

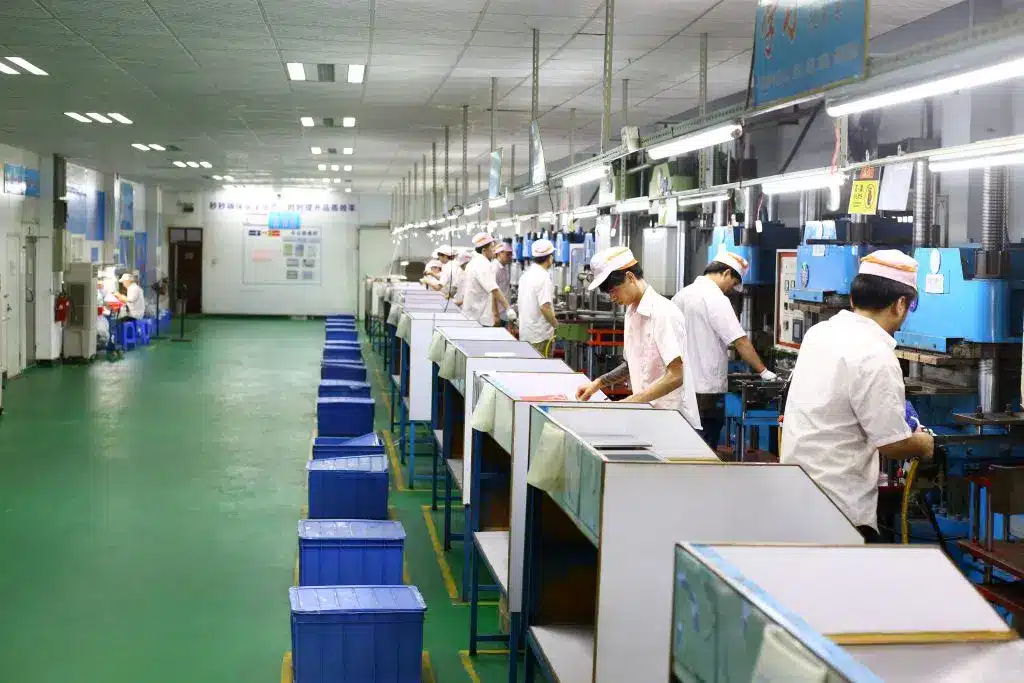
Quality Inspection:
Finished silicone products undergo rigorous quality inspections, including those for appearance, dimensional accuracy, and hardness. Any defects or substandard products are promptly identified and addressed.
Post-processing and Packaging:
Qualified silicone products undergo post-processing, including cleaning and trimming, before being packaged. During packaging, care must be taken to preserve the appearance and quality of the silicone products and ensure they are not damaged during transportation and storage.

Silicone extrusion molding
The raw materials are squeezed through an extruder to form tubular and strip-shaped products, such as silicone tubing and sealing strips.
Extrusion molding is a continuous production process for silicone products. The raw silicone material is squeezed into the desired shape through an extruder, and then cooled and cut into the final product. The specific steps are as follows:
Raw Material Preparation: Similar to the compression molding process, raw silicone, vulcanizing agent, masterbatch, and other raw materials are mixed and refined.
Extruder Commissioning: Based on the shape and size of the silicone product, an appropriate extruder is selected and commissioned. An extruder typically consists of a screw, barrel, die, and heating device.
Extrusion Molding:
The mixed silicone raw materials are added to the extruder.
The rotating screw gradually pushes the silicone raw materials toward the die.
There, the silicone raw materials are extruded through a die into the desired shape.

Cooling and Cutting: Extruded silicone products undergo cooling and cutting processes. Cooling can be done with water or air to rapidly solidify the silicone product. Cutting can be done manually or automatically to cut the silicone product into the desired length.
Extrusion molding offers advantages such as high production efficiency, consistent product shape, and suitability for continuous production. However, this process also has some disadvantages, such as relatively low product dimensional accuracy and high mold costs.
Solid silicone calendering molding
The raw material is pressed into sheets or plates using a calender, suitable for simple products such as silicone gaskets and tapes. The silicone calendering process mainly includes the following steps:
Raw Material Preparation:
The raw materials undergo compounding and plasticization, then are extruded into a shaped sheet through an extruder, preparing it for subsequent calendering.
Calendering:
The rubber material is fed into a calender, where it is pressed through rollers to form a sheet or film of uniform thickness. This process allows for controlled thickness (typically ranging from 0.05-1.00 mm) and the ability to manipulate surface textures.
Post-Processing:
After forming, the product undergoes cooling, drawing, and slitting before being wound into a coil or cut into specific shapes.
Some products require die-cutting to achieve their final shape.

This process is suitable for producing sheet products such as silicone gaskets, coils, and films. It features continuous production and high dimensional accuracy, but the equipment costs are relatively high.
Cutting and forming
Die-cutting and laser cutting are used to cut silicone sheets into specific shapes, such as spacers and rubber gaskets. Die-cutting utilizes a press, die, and punch to cut silicone sheets according to pre-designed templates. This process is suitable for products with low hardness, and shapes are no longer limited to straight edges or right angles. Typical products include rubber gaskets and spacers. Laser cutting uses a cutting machine to cut silicone sheets into various sizes and shapes. It is suitable for precision products requiring high precision, without size restrictions. Typical products include flange gaskets. Advantages of this process include high production efficiency, simple production, and precise product dimensions. Disadvantages include high material loss.

How to produce TPU products?
TPU product manufacturing methods include injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, and recycling.
1.Injection Molding: Injection molding involves injecting molten TPU material into a mold, cooling it, and solidifying it into the desired product. Injection molding is suitable for producing TPU products with complex shapes and precise dimensions, such as shoe soles and automotive parts.
2. Extrusion: Extrusion involves extruding molten TPU material through a molding nozzle, cooling and solidifying it to produce the desired product. Extrusion is suitable for producing long, thin, or tubular TPU products, such as sealing strips and hoses.
3. Calendering: Calendering involves pressing molten TPU material through a rolling or calendering mechanism to form the desired product. Calendering is suitable for producing single-layer or multi-layer thin TPU products, such as packaging films and sound insulation materials.

Process:
- Raw Material Preparation: Select suitable TPU raw materials and perform pre-treatment as required, such as pellet crushing and drying.
- Material Proportioning: Precisely mix the TPU raw materials and other auxiliary materials, such as plasticizers, stabilizers, and colorants, according to product requirements.
- Melt Mixing: Feed the precisely proportioned raw materials into the melter for mixing and melting until they reach a state suitable for molding.
- Molding: Select the appropriate molding method, such as injection molding, extrusion, or calendering, based on the specific product requirements.
- Cooling and Curing: Cool the molded TPU material to rapidly solidify it, maintaining the desired shape and size.
- Secondary Processing: As needed, perform secondary processing such as trimming, cutting, and polishing on the molded TPU product to achieve the final product specifications.
Features: High production efficiency, easy secondary processing, and low mold costs.

How Much of Silicone VS TPU?
Silicone is in high demand in the high-end market, requiring higher quality, and therefore relatively more expensive. TPU, on the other hand, may have a larger market share in the mid- and low-end markets, offering more affordable prices.
If you require custom silicone products, Z.S.R will provide you with the best pricing, attentive service, and high-quality products.
Custom Silicone Products | OEM/ODM Service
How to Choose Silicone VS TPU?
The choice between TPU and silicone should be determined based on key performance indicators for the specific application, including mechanical properties, temperature resistance, and chemical stability:
Mechanical Properties and Temperature Resistance
- TPU: Features a high elastic modulus (Shore A 60-95), a wide hardness range, excellent wear resistance, and a temperature resistance range of -40°C to 80°C (some models reach 120°C). It is suitable for applications requiring frequent deformation or wear and tear, such as sports equipment, shoe soles, and phone cases.
- Silicone: Features lower elasticity (Shore A 10-80), but a wider temperature resistance range (-60°C to 230°C) and outstanding high-temperature stability, making it suitable for applications requiring extreme temperature resistance, such as medical devices and kitchen utensils.
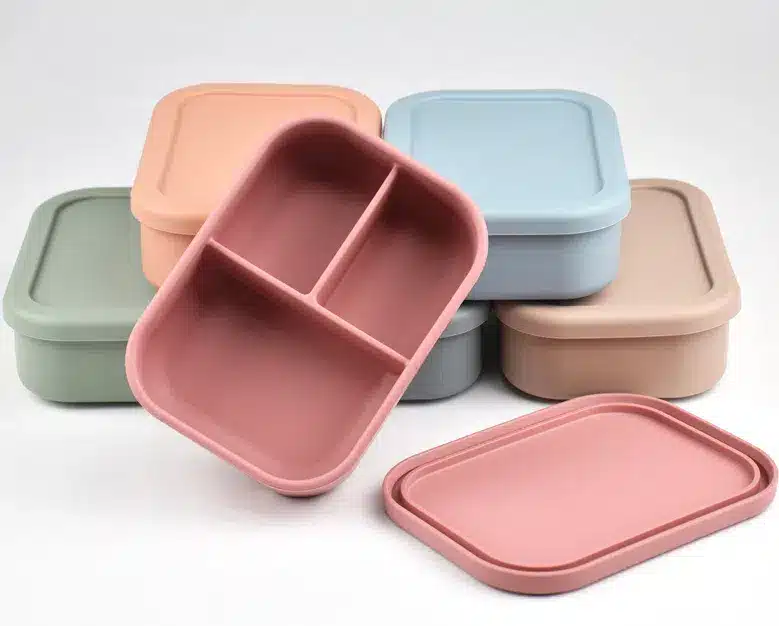

Chemical Stability
- TPU: Oil- and hydrolysis-resistant, but long-term exposure to grease or UV rays may degrade its performance, making it unsuitable for outdoor use or oily environments.
- Silicone: Acid-, alkali-, and UV-resistant, with strong chemical stability, making it suitable for applications requiring high hygiene, such as medical devices and baby products.

Applications
- TPU: Phone cases (cushioning performance, wear resistance), sports equipment (elasticity), automotive parts (oil resistance)
- Silicone: Kitchenware (high-temperature resistance), seals (high-temperature stability), medical devices (hygiene)
TPU is preferred for lightweight, transparent, and easy-to-process materials. Silicone is preferred for high-temperature stability, hygienic safety, or outdoor durability.

How to Control Silicone products quality?
The quality control of silicone products requires full control of the entire process from raw material control, process optimization to finished product inspection. The following are the key control points:
Raw Material Quality Control
- Supplier Audit: Select ISO-certified raw material suppliers, requiring certifications such as FDA/LFGB. Each batch of raw materials must include a Certificate of Analysis (COA) and transportation temperature and humidity records.
- Testing Standards: Incoming testing: Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) ≤ 0.01ppm, hardness deviation ±5 Shore A.
- Storage Management: Warehouses must be dry and dark, and a first-in, first-out principle must be implemented to ensure raw materials are used within their expiration dates.
- Production Process Optimization
- Formulation Design: Adjust the silicone oil content based on product characteristics (typically molding at 170-230°C) to ensure fluidity and deformation resistance. • Molding Parameters:
- Injection Molding: Temperature 170-230°C, Pressure 8-15 MPa, Speed 15-25 g/s
- Compression Molding: Mold Temperature 160-180°C, Venting 0.5-1 per square centimeter

Post-Processing: Vulcanization Temperature ±2°C, Secondary Vulcanization for Industrial Products at 200°C for 4 hours, Stepwise Curing for Medical Products (120°C for 1 hour → 150°C for 2 hours)
Finished Product Inspection
- Appearance Inspection: No bubbles or scratches on the surface, and color/transparency meet standards.
- Physical Properties: Hardness, tensile strength, tear strength, and other indicators must meet national standards.
- Chemical Testing: Acid and alkali resistance, aging resistance testing. Medical-grade products must pass ISO 10993 biocompatibility testing.
How to Control TPU Products quality?
Quality control for TPU products requires multiple aspects, including raw material selection, processing technology, and environmental control.
Raw Material Quality Control
Select TPU materials that meet standards to ensure basic properties such as elasticity, temperature resistance, and chemical resistance meet standards. Avoid using raw materials that contain impurities or are not fully plasticized to prevent problems such as surface non-melting points and powder seepage.
Process Optimization
- Temperature Control:
- Set the processing temperature based on the TPU material’s characteristics to avoid excessively high or low temperatures that could cause deformation or insufficient bonding. For example, hot melt adhesive bonding requires precise control of the temperature around 120°C, ensuring uniform temperature across the entire bonding area.
- Pressure Adjustment:
- Adjust the pressure based on the product’s thickness and surface area to avoid excessive pressure that could cause material thinning or marking.
- Forming Process:
- Products such as elastic bands require baking and tempering to reduce bending and tangling.

Environmental and Storage Management
Avoid prolonged exposure to high temperatures and high humidity. Store in a dry, dark environment to prevent UV damage and chemical infiltration.
Finished Product Inspection
Implement strict quality control, including raw material inspection, semi-finished product spot checks, and finished product performance testing, to promptly identify and resolve potential issues.
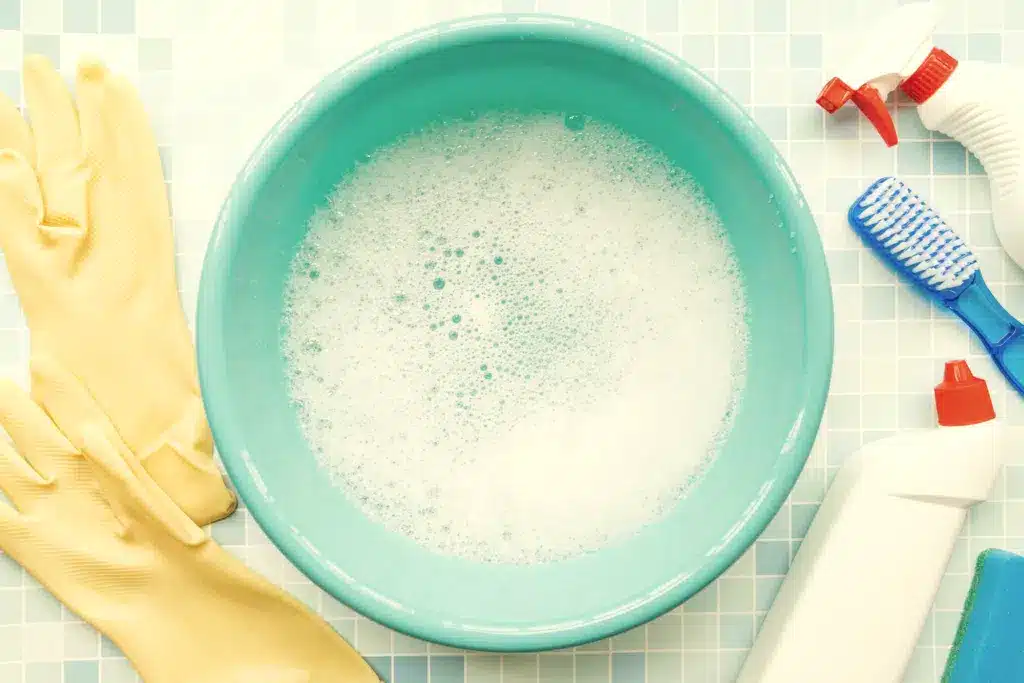
How to Clean Silicone products and TPU silicone?
Silicone: Boilable, high-temperature sterilizable, and dishwasher-safe.
TPU: Clean with warm water or 70% alcohol, not heat-resistant.
Regular cleaning is recommended, and cleaning instructions are provided in the product instructions.

More FAQs
Summary
In summary, the key to material selection lies in a comprehensive decision: the product’s usage environment, desired feel, and cost budget. Silicone is preferred for applications requiring a superior feel, high temperature resistance, and suitable for hygienic or skin-friendly applications.
TPU is the preferred material for applications requiring wear resistance, structural robustness, and cost control, suitable for mass-produced consumer electronics and outdoor applications. If you have questions about your project and the materials you need, please contact our Z.S.R. for further evaluation.
Further Reading
Technical Related
About Author: Z.S.R International Group
Z.S.R International Group(Hong Kong) co., Limited, is a one-stop supplier for molded silicone products and silicone products molding solution provider in the consumer products field. We offer OEM services from silicone product design to Silicone products contract manufacturing. We have the capability for custom silicone tooling, LSR(Liquid silicone Rubber) molded silicone products, solid silicone molded products, molded silicone multi-colored products. We also can custom molded silicone, custom molded LSR, custom molded dripping injection dispensing(co-injection) silicone multi-colored products.